Implementing Queue Data Structure Algorithm in Python: A Detailed Guide
Last updated: September 13, 2024 By Sunil Shaw

Introduction
In a Queue Data Structure, objects form a sequence where elements added at one end and removed from the other end. The queues follow the principle of first in first out. One end, referred to as the Front, removes items while the other end, referred to as the Rear, has items removed from it. Items enter the queue from the rear, moving forward as each item is removed in front. Let’s see how to Implementing Queue Data Structure Algorithm in Python: A Detailed Guide.
So, in queue the item at the front is the one end that has been in the sequence for the longest and the most recently added item must wait at the end. You enqueue for insert operations and dequeue for delete operations.
What is Return Statement in Python : Syntax and Usage
Basic queue functions
Basic Queue functions are as follows:
- enqueue(i): Add element
ito the queue. - dequeue(): Removes the first element from the queue and returns its value.
- isEmpty(): Boolean function that returns
trueif the queue is empty else it will return false. - size(): Returns length of the queue.

Implementation of Queue Data Structure Algorithm in Python
Let’s write a program for implementation of queue.
Step1: Define the class
class Queue:Step2: Define the construction
Here, we initialize an empty list queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []Step3: Define isEmpty() function
As the name suggests, this method is called to check if the queue is empty or not. TheisEmpty() function checks the queue. If it is empty, it prints a message – Queue is not Empty.
def isEmpty(self):
if self.queue == []:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
print("Queue is not Empty")Step4: Define the enqueue() function
This function takes an element as parameter and inserts it at index 0 . All elements in the queue shift by one index.
def enqueue(self, element):
self.queue.insert(0, element)Step5: Define the dequeue() function
This below function code pops the oldest element from the queue.
def dequeue(self):
self.queue.pop()Step6: Define the size() function
This function returns the length of the queue.
def size(self):
print("size of queue is", len(self.queue))Step7: Write down the commands to execute the code
Execution/Driver Code
print("inserting element no. 1")
q.enqueue("apple")
print("inserting element no. 2")
q.enqueue("banana")
print("inserting element no. 3")
q.enqueue("orange")
print("The queue elements are as follows:")
print(q.queue)
print("check if queue is empty?")
q.isEmpty()
# removing elements
print("remove first element")
q.dequeue()
print("what is the size of the queue?")
q.size()
print("print contents of the queue")
print(q.queue)
Main Code
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def isEmpty(self):
if self.queue == []:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
print("Queue is not empty")
def enqueue(self, element):
self.queue.insert(0, element)
def dequeue(self):
self.queue.pop()
def size(self):
print("size of queue")
#Code Execution
q = Queue()
q.isEmpty()
# inserting elements
print("inserting element no. 1")
q.enqueue("apple")
print("inserting element no. 2")
q.enqueue("banana")
print("inserting element no. 3")
q.enqueue("orange")
print("The queue elements are as follows:")
print(q.queue)
print("check if queue is empty?")
q.isEmpty()
# removing elements
print("remove first element")
q.dequeue()
print("what is the size of the queue?")
q.size()
print("print contents of the queue")
print(q.queue)
Output
Queue is Empty
inserting element no. 1
inserting element no. 2
inserting element no. 3
The queue elements are as follows:
['orange', 'banana', 'apple']
check if queue is empty?
Queue is not empty
remove first element
what is the size of the queue?
size of queue
print contents of the queue
['orange', 'banana']Implementation of a stack using single queue
Before implementing the code, it is important to understand the logic behind it. The question explains that you make a queue work like a stack. A queue data structure works on the principle of First-In-First-Out whereas a stack works on the principle of Last In, First Out.
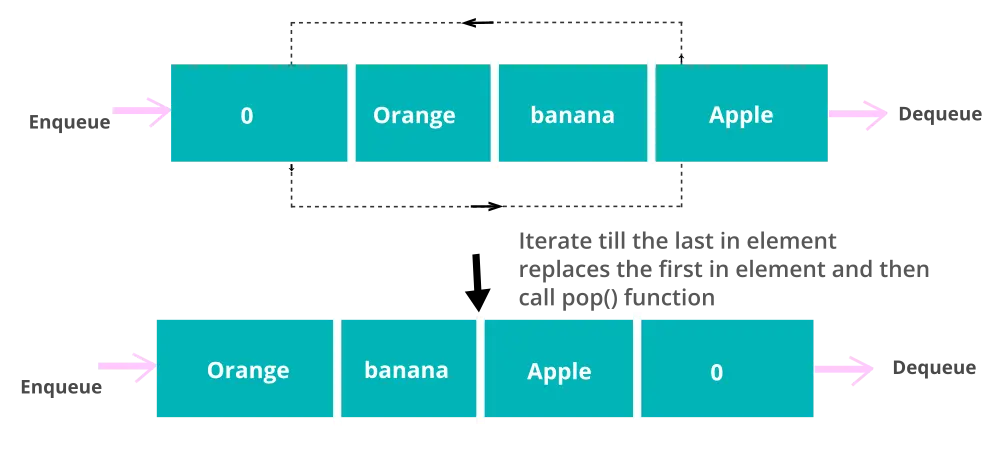
class Stack_from_Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def isEmpty(self):
if self.queue == []:
print("Queue is Empty")
else:
print("Queue is not empty")
def enqueue(self, element):
self.queue.insert(0, element)
def dequeue(self):
return self.queue.pop()
def size(self):
print("size of queue is", len(self.queue))
def pop(self):
for i in range(len(self.queue)-1):
x = self.dequeue()
print(x)
self.enqueue(x)
print("element removed is", self.dequeue())Execution – 1
sq = Stack_from_Queue()
sq.isEmpty()
print("inserting element apple")
sq.enqueue("apple")
print("inserting element banana")
sq.enqueue("banana")
print("inserting element orange")
sq.enqueue("orange")
print("inserting element 0")
sq.enqueue("0")
print("The queue elements are as follows:")
print(sq.queue)
print("check if queue is empty?")
sq.isEmpty()
print("remove the last in element")
sq.pop()
sq.pop()
sq.pop()
sq.pop()
sq.isEmpty()Output – 1
Queue is Empty
inserting element apple
inserting element banana
inserting element orange
inserting element 0
The queue elements are as follows:
['0', 'orange', 'banana', 'apple']
check if queue is empty?
Queue is not empty
remove the last in element
apple
banana
orange
element removed is 0
apple
banana
element removed is orange
apple
element removed is banana
element removed is apple
Queue is EmptyExecution – 2
sq = Stack_from_Queue()
sq.isEmpty()
print("inserting element apple")
sq.enqueue("apple")
print("inserting element banana")
sq.enqueue("banana")
print("inserting element orange")
sq.enqueue("orange")
print("inserting element 0")
sq.enqueue("0")
for i in range(len(sq.queue)):
print("The queue elements are as follows:")
print(sq.queue)
sq.pop()
print("check if queue is empty?")
sq.isEmpty()
print("remove the last in element")
print(sq.queue)Output – 2
Queue is Empty
inserting element apple
inserting element banana
inserting element orange
inserting element 0
The queue elements are as follows:
['0', 'orange', 'banana', 'apple']
apple
banana
orange
element removed is 0
check if queue is empty?
Queue is not empty
remove the last in element
['orange', 'banana', 'apple']
The queue elements are as follows:
['orange', 'banana', 'apple']
apple
banana
element removed is orange
check if queue is empty?
Queue is not empty
remove the last in element
['banana', 'apple']
The queue elements are as follows:
['banana', 'apple']
apple
element removed is banana
check if queue is empty?
Queue is not empty
remove the last in element
['apple']
The queue elements are as follows:
['apple']
element removed is apple
check if queue is empty?
Queue is Empty
remove the last in element
[]Implementation of a queue using two stacks
Let’s see how to implement a queue using two stacks.
Step1:
Create a basic Stack() class with push(), pop() and isEmpty() functions.
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def push(self, element):
self.stack.append(element)
def pop(self):
return self.stack.pop()
def isEmpty(self):
return self.stack == []Step2: Define the Queue class
class Queue:Step3: Define the constructor
Since the requirement here is of two stacks, we initialize two stack objects.
def __init__(self):
self.inputStack = Stack()
self.outputStack = Stack()Step4: Define the enqueue function
This function will push the elements into the first stack.
def enqueue(self, element):
self.inputStack.push(element)Step5: Define the dequeue() function
This function checks whether the output stack is empty. If it is empty, then elements will be popped out from input Stack one by one and pushed into the output Stack, so that the last in element is the first one to be out. On the other hand, if the output stack is not empty, then the elements can be popped directly from it.
Now, suppose we insert 4 values: 1,2,3,4 calling the above enqueue function. Then, the input stack would be like this.
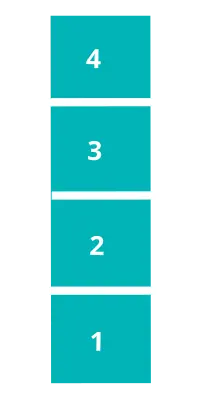
When we call a dequeue function, the elements from inputStack are popped and pushed one by one on the output stack till we reach the last element and that last element is popped from the inputStack and returned. If the output stack is not empty then it means that it already has elements in the right order and they can be popped in that order.
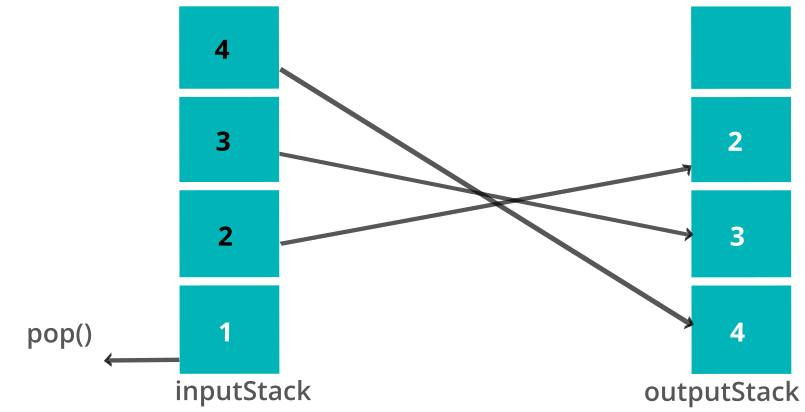
def dequeue(self):
if self.outputStack.isEmpty():
for i in range(len(self.inputStack.stack)-1):
x = self.inputStack.pop()
self.outputStack.push(x)
print("popping out value =", self.inputStack.pop())
else:
print("popping out value =", self.outputStack.pop())Full Code
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.inputStack = Stack()
self.outputStack = Stack()
def enqueue(self, element):
self.inputStack.push(element)
def dequeue(self):
if self.outputStack.isEmpty():
for i in range(len(self.inputStack.stack)-1):
x = self.inputStack.pop()
self.outputStack.push(x)
print("popping out value =", self.inputStack.pop())
else:
print("popping out value =", self.outputStack.pop())
# Define Stack Class
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def push(self, element):
self.stack.append(element)
def pop(self):
return self.stack.pop()
def isEmpty(self):
return self.stack == []
Output
q = Queue()
print("insert value 1")
q.enqueue(1)
print("insert value 2")
q.enqueue(2)
print("insert value 3")
q.enqueue(3)
print("insert value 4")
q.enqueue(4)
print("dequeue operation")
q.dequeue()
q.dequeue()
print("insert value 7")
q.enqueue(7)
q.enqueue(8)
q.dequeue()
q.dequeue()
q.dequeue()
q.dequeue()A Journey into the World of Python
So here you learned how to Implementing Queue Data Structure Algorithm in Python: A Detailed Guide
About Author
I am a Web Developer, Love to write code and explain in brief. I Worked on several projects and completed in no time.
View all posts by Sunil Shaw1 comment
-
Pingback: How to implement Linked List Data Structure Using Python - CodeWithRonny